Drive growth with enterprise cybersecurity: top threats, frameworks, Zero Trust, AI and ROI tactics for USA, UK, Canada & Australia-plus jobs and tools.
Enterprise cybersecurity is no longer a defensive checkbox—it’s a growth lever. In Tier One markets like the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia, boards now tie security maturity directly to revenue, valuation, and market access. Buyers want proof of resilience, regulators demand verifiable controls, and partners expect airtight supplier risk management. The pain is clear: sprawling cloud estates, hybrid work, AI-fueled attacks, and talent gaps increase risk exposure while slowing sales and inflating costs. Yet the promise is powerful: when enterprises treat cybersecurity as a go-to-market advantage, they unlock faster procurement cycles, better insurance terms, lower incident costs, and higher conversion rates by demonstrating trust at every touchpoint.
Imagine a UK fintech entering North America. In six months, it maps its controls to NIST/ISO, publishes transparent security pages, hardens identity and endpoint baselines, and automates evidence for audits. Not only do breach risks drop, but sales velocity climbs 22% as procurement teams green-light deals faster. A Canadian SaaS vendor implements Zero Trust and continuous monitoring; MTTD/MTTR drop, insurance premiums fall, and enterprise buyers push them onto preferred vendor lists. An Australian manufacturer consolidates tooling, reduces alert fatigue, and turns compliance into one-click reporting—freeing teams to focus on threat hunting and product security.
Key promise: This guide shows how to translate major concepts of enterprise cybersecurity into measurable ROI—more leads, cleaner audits, higher close rates, and resilient growth. You’ll see practical architectures, frameworks, and playbooks used by enterprise cybersecurity companies, plus a clear view of enterprise cybersecurity jobs shaping 2025 teams. Takeaway: Treat security as a trusted product feature and your pipeline will feel the lift.
Top Cyber Threats Facing Enterprises Today: Risk, ROI, and Business Continuity
Modern enterprises face a blended threat picture: ransomware-as-a-service, business email compromise, supply-chain compromises, API abuse, cloud misconfigurations, and AI-powered social engineering. Each risk has a business math: incident probability × impact (regulatory fines, outage costs, churn, legal exposure). The smartest CISOs model this in quarterly risk councils and allocate budget based on expected loss avoided—that’s the ROI conversation executives understand.
Mini Case Study – USA (Healthcare SaaS):
A US healthcare SaaS platform endured repeated credential-stuffing attacks driving costly support tickets and SSO instability. By enforcing phishing-resistant MFA, implementing risk-based conditional access, and tightening API rate limiting, support tickets fell 41%, churn decreased 6%, and an enterprise deal previously stuck in security review closed in 28 days. Security work funded itself.
Threat-to-ROI Table
| Threat Vector | Business Impact | High-ROI Mitigation | Near-Term ROI Signal |
| Ransomware | Downtime, data exfiltration | Immutable backups, EDR, least privilege | Lower insurance premiums |
| BEC/Invoice Fraud | Direct financial loss | DMARC/DKIM/SPF, payment verification | Fewer loss events, audit pass |
| Cloud Misconfig | Data exposure, fines | CSPM + IaC guardrails | Faster audits, fewer Sev-1s |
| Third-Party/Supply Chain | Regulatory & reputational risk | TPRM automation, SBOM | Faster vendor approvals |
| API Abuse | Revenue leakage | WAF, anomaly detection, auth hardening | Reduced fraud/refunds |
Key Tip: Convert every critical risk into a dashboarded $/hour estimate tied to MTTD, MTTR, downtime, and churn. Sales and Finance will champion the roadmap.
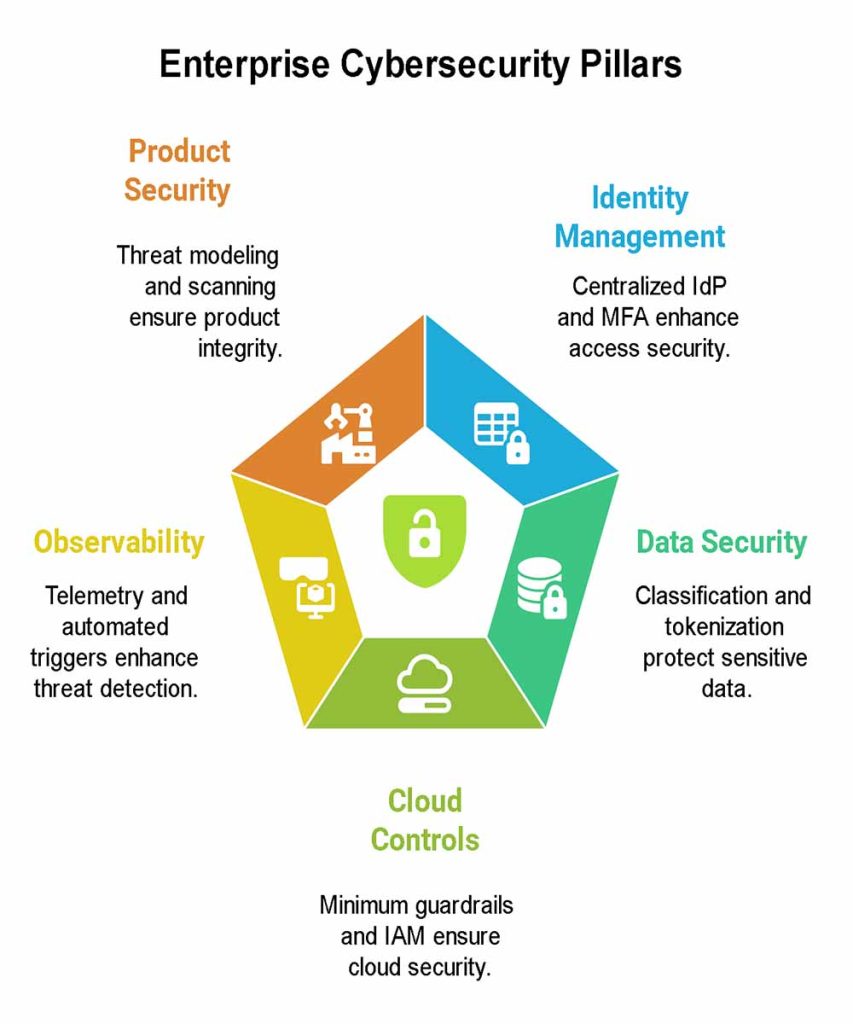
Core Principles of Enterprise Cybersecurity Architecture: Protecting Tier One Businesses
Enterprise architecture keeps complexity from eroding risk controls. In Tier One markets, the reference playbook blends Zero Trust, identity-first security, defense-in-depth, and secure-by-default engineering. Start from identity, encrypt data at rest/in transit, segment networks, adopt continuous verification, and treat production change as a governed pipeline activity.
Architecture Snapshots:
- Identity as the new perimeter: Centralized IdP, phishing-resistant MFA, device trust, just-in-time access, admin elevation recording.
- Data-centric security: Classification, DLP, key management (KMS/HSM), tokenization for sensitive fields, data lineage visibility.
- Cloud baseline controls: Minimum guardrails (CIS benchmarks), policy-as-code, drift detection, and least privilege IAM with periodic recertification.
- Observability for security: Telemetry from endpoints, cloud, apps, and identity; detections written as code; automated containment triggers.
- Product security: Threat modeling, SAST/DAST/IAST, SBOMs, secrets scanning, and release gates linked to severity thresholds.
Architecture-to-Outcome Table
| Principle | Concrete Control | Growth/ROI Impact |
| Zero Trust | Per-request authZ, device posture | Fewer breaches, easier enterprise deals |
| Least Privilege | Role design, JIT elevation | Limits blast radius, audit confidence |
| Security as Code | OPA/Policy-as-Code, IaC scans | Fewer misconfigs, faster releases |
| Resilience | Immutable backups, chaos testing | Lower downtime cost, premium relief |
| Transparency | Public security page, trust center | Faster procurement, higher conversions |
Takeaway: Architecture is sales enablement. Show the diagram; win the deal.
Enterprise Cybersecurity Frameworks for Compliance, Trust, and Growth
Frameworks translate strategy into repeatable execution. NIST CSF, ISO/IEC 27001, SOC 2, CIS Controls, and sector regimes (HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR/UK GDPR, Australian Privacy Act) establish shared language across IT, Legal, Sales, and customers. The win? Streamlined security questionnaires, shorter audits, and predictable investment.
Mini Case Study – UK (Fintech):
A London fintech mapped controls to ISO 27001 and NIST CSF; automated evidence collection via a GRC tool; published a living Trust Center. Average security questionnaire time dropped from 18 hours to 3. Deals cleared procurement 26% faster.
Framework Fit Table
| Framework | Best For | Proof That Sells |
| NIST CSF | Broad maturity roadmap | Tiered target state + metrics |
| ISO 27001 | International certification | Certificate + SoA + audit letters |
| SOC 2 | SaaS buyers in US | Type II report + Trust Services Criteria |
| CIS Controls | Practical control set | Quick wins dashboard |
| PCI DSS/HIPAA | Regulated sectors | ROC/AOC, HIPAA program evidence |
Key Tip: Choose one primary framework for governance, then map others as “crosswalks.”
Key Challenges in Enterprise Cybersecurity and How to Overcome Them
Common barriers: tool sprawl, alert fatigue, talent shortages, siloed budgets, and shadow IT. Overcoming them requires consolidation, automation, and culture.
Mini Case Study – Canada (Retail):
A national retailer reduced 27 security tools to 12, integrated logging, and built a unified triage queue. Analyst productivity rose 35%, false positives fell, and MTTR improved 44%.
Challenge-to-Remedy Table
| Challenge | Remedy | ROI Signal |
| Tool Sprawl | Platform consolidation, shared data layer | Lower licensing, faster investigations |
| Alert Fatigue | Risk scoring, automation, playbooks | Higher analyst throughput |
| Skills Gap | Upskilling programs, mentorship ladders | Better retention, fewer escalations |
| Shadow IT | App registry, CASB discovery | Lower data exposure, cleaner audits |
| Budget Silo | Risk council with Finance | Spend tied to loss avoidance |
Continuous Monitoring: Driving Enterprise Trust & Conversion with Proactive Security
Continuous monitoring turns security from reactive to predictive. Aggregate telemetry from identity, endpoint, network, app, and cloud. Normalize events, write detections as code, test them, and track drift. Present weekly delta reports to product and operations so issues get fixed before audits—or attackers—find them.
Pros/Cons Table
| Approach | Pros | Cons |
| Centralized SIEM + SOAR | Unified view, automated response | Requires curation & tuning |
| Federated Monitoring | Local autonomy | Risk of blind spots |
| Managed Detection & Response | Speed to value | Vendor transparency varies |
Expert Insight: Enterprises that version-control detections and run unit tests on analytics see fewer false positives and faster incident learning.
Least Privilege Strategy: Reducing Risk While Maximizing ROI
Least privilege reduces blast radius. Move from “access by default” to “access by need and time.” Model roles narrowly, rotate keys, rotate secrets, and document a break-glass pathway with logging.
Pros/Cons Quick View
| Benefit | Consideration |
| Smaller attack surface | Requires identity governance discipline |
| Faster audits | Initial role engineering effort |
| Lower insider risk | Cultural shift: fewer standing privileges |
Expert Insight: Pair least privilege with JIT elevation and you’ll meet security and developer productivity goals.
Zero Trust Architecture: Enhancing Enterprise Cybersecurity Growth
Zero Trust isn’t a product; it’s a verification posture. Authenticate/authorize every request, validate device health, enforce segmentation, and log everything. Start with identity, device, and network micro-segments; then move up-stack to application-level policies.
Outcome Table
| ZTA Step | Quick Win | Sales Impact |
| Phishing-resistant MFA | Stops common BEC paths | Insurance & buyer confidence |
| Device Posture Checks | Block risky access | Fewer incidents → better SLA |
| Micro-segmentation | Contain lateral movement | Persuades security reviewers |
AI in Cybersecurity: How Artificial Intelligence Assists Attackers and Defenders
Attackers leverage AI for phishing at scale, credential stuffing optimization, and malware obfuscation. Defenders use AI for behavior analytics, alert enrichment, fraud detection, and automated playbooks. The winning posture is human-in-the-loop: analysts validate AI suggestions, tune thresholds, and document precision/recall.
Pros/Cons Matrix
| AI for Defense | Strength | Watchout |
| Anomaly Detection | Finds weak signals | Drift & noisy baselines |
| Summarization | Speeds triage | Hallucinations if unchecked |
| Auto-Remediation | Rapid containment | Scope errors without guardrails |
Expert Insight: Track false positive rate and time saved per incident to justify AI investments to Finance.
What is Enterprise Cybersecurity? Complete Guide for Global Enterprises
Enterprise cybersecurity is the organizational capability to prevent, detect, respond to, and recover from cyber risk while supporting business goals. It spans people, process, technology, and evidence. For global enterprises, it also means cross-border data rules, vendor dependencies, and M&A integration.
Quick Checklist (Tier One Ready)
- Security strategy aligned to revenue goals
- Framework selection + control mapping
- Identity-first controls + device posture
- Continuous monitoring + tested IR plan
- Transparency: Trust Center + customer artifacts
Micro-CTA: Turn the list into a quarterly scorecard shared with Sales, Legal, and Product.
What are the 3 Most Common Cybersecurity Problems in Enterprises Today?
- Identity sprawl: multiple IdPs, shadow accounts, stale privileges.
- Cloud misconfigurations: public buckets, permissive roles, untagged resources.
- Third-party risk: vendor compromises and poor SBOM visibility.
Tip: Remediate in that order to cut breach likelihood fastest.
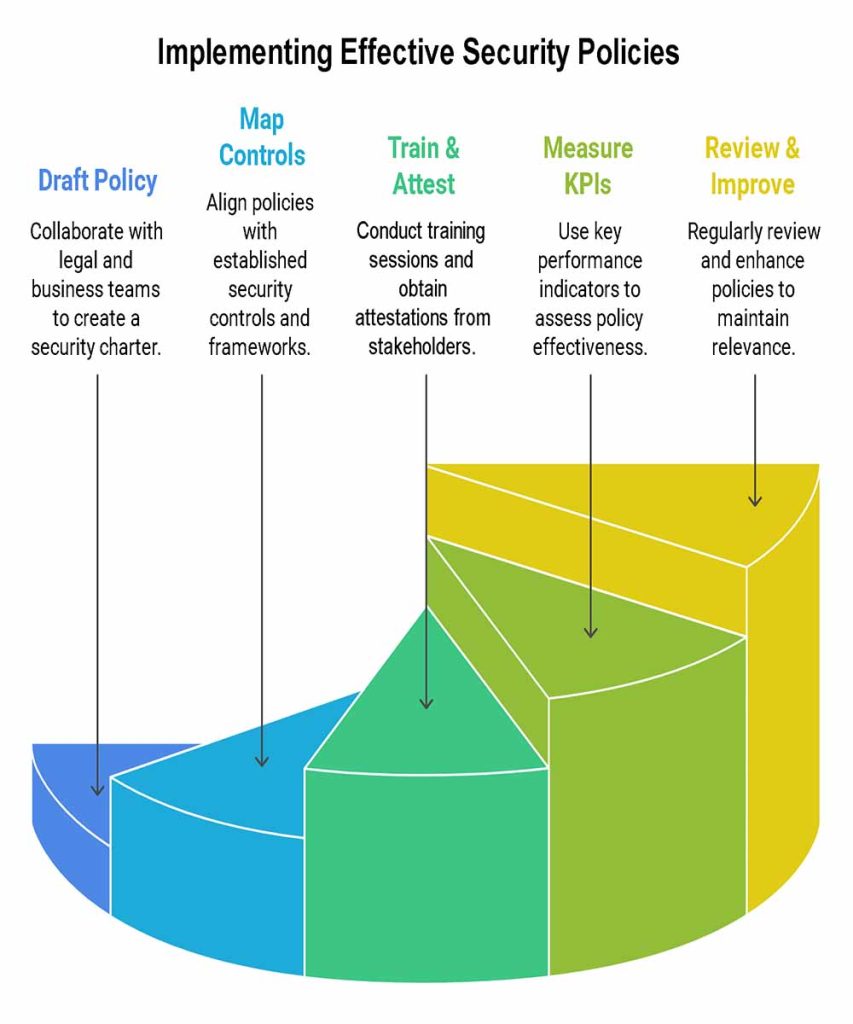
“What is Enterprise Policy in Cybersecurity? Step-by-Step Compliance Guide”
Policy turns intent into instruction. Start with a security charter, then write concise, testable policies: Access Control, Acceptable Use, Data Classification, Incident Response, Vulnerability Management, Change Management, Vendor Risk, and Backup/Recovery.
Policy Steps
- Draft (owner + legal + business)
- Map to controls and frameworks
- Train & attest
- Measure with KPIs
- Review and improve quarterly
What is an Enterprise Security System? ROI-Driven Overview for Tier One Businesses
It’s the interlock of identity, endpoint, network, cloud, data, and observability—all governed by policies and supported by skilled people. The ROI comes from fewer incidents, faster audits, and faster sales.
System View
| Layer | Example Capability | ROI |
| Identity | SSO + MFA + JIT | Less fraud, faster onboarding |
| Endpoint | EDR + device trust | Containment without outages |
| Cloud | CSPM + IaC guardrails | Fewer Sev-1s |
| Data | DLP + KMS | Fewer disclosures |
| Observability | SIEM + SOAR | Faster MTTR |
CISO Burnout: Balancing Leadership, Pressure, and ROI in Enterprise Cybersecurity
CISOs carry weight: breach accountability, 24/7 alerts, budget scrutiny, and hiring hurdles. Burnout risks include decision fatigue and over-rotation to firefighting.
Quick Remedies
- Delegate run ops to detection engineering leads
- Establish a risk council with Finance and Legal
- Quarterly no-blame postmortems
- Career ladders and rotations to retain talent
AI-Powered Attacks: What CISOs in Tier One Countries Must Know Now
Expect hyper-realistic phishing, deepfake voice fraud, and automated recon. Defenses: user awareness with real examples, phishing-resistant MFA, payment change verification, and voiceback procedures for high-risk approvals.
Tiny Table
| Attack | Defense |
| Deepfake CFO call | Dual-control + callback to stored number |
| AI recon of staff | Minimize public attack surface |
| Synthetic phishing | Behavioral detections + training |
RSA Conference Wrap-Up: The State of Enterprise Cybersecurity Disconnect
Themes: platform consolidation, AI on both sides, SBOMs in software supply chains, and identity as the soft underbelly. The disconnect? Many orgs buy tools before fixing role design, logging quality, and patch governance.
Takeaway: Start with foundations; tools amplify good processes but won’t replace them.
Micro-CTA: Use conference takeaways to prune the roadmap, not inflate it.
Enterprise Case Study: How Global Organizations Achieve ROI Through Cybersecurity Best Practices
A global SaaS vendor aligned to NIST CSF, implemented Zero Trust, and built a Trust Center. Security questionnaires now auto-resolve 60% of controls. Deals over $500k used to stall for 90 days; now the median is 34 days. A single ransomware incident averted saved millions; the CFO now treats security as margin protection.
Result: Security became a sales asset and a cost shield.
On-Prem Enterprise Cybersecurity Solutions: ROI & Trust Factors
On-prem isn’t dead—regulated industries and latency-sensitive workloads persist. ROI comes from asset criticality mapping, network segmentation, and EDR with isolation. Trust factors: physical security, rigorous change control, and tested backup/restore.
Recap: Invest where blast radius is biggest; measure ROI as downtime avoided × revenue/hour.
Cloud Security Services: Driving Enterprise Conversions in USA & UK
US and UK buyers expect mature cloud controls: CSPM/CIEM, workload protection, IaC scanning, key management, and posture dashboards. Publish your cloud shared responsibility model and customer-facing diagrams. Sales accelerates when security is transparent.
Cybersecurity Advisory Services: ROI Benefits for Tier One Enterprises
Advisory partners accelerate roadmaps: virtual CISO, red/purple teams, tabletop exercises, and compliance readiness. The ROI shows up in fewer findings, quicker deal cycles, and fewer renewal risks.
Tip: Contract for knowledge transfer—you’re not buying hours; you’re buying uplift.
Strictly Necessary Cookies & Data Privacy Compliance: Enterprise Perspective
Privacy programs must align cookies with consent and purpose limitation. Mark strictly necessary cookies clearly and segregate from marketing tags. Adopt a CMP (consent management platform) and log consent for audit trails across the USA, UK, Canada, Australia privacy regimes.
Recap: Transparent privacy UX builds trust and removes objections in security questionnaires.
FAQs:
What is the role of enterprise cybersecurity in risk management and ROI?
Enterprise cybersecurity quantifies risk (likelihood × impact) and prioritizes controls that reduce expected loss. When you cut MTTD/MTTR, prevent fraud, and avoid outages, you directly improve margin and revenue stability. Tie initiatives to dollars per hour of downtime, premium reductions, and deal velocity from faster security reviews. With dashboards that track incidents avoided, patch SLAs, control coverage, and audit readiness, CISOs can show Finance how security spend returns multiples via loss avoidance and conversion gains.
What is corporate cybersecurity and how does it differ from enterprise cybersecurity?
Corporate cybersecurity often refers to the company-wide baseline—policy, awareness, and IT hardening. Enterprise cybersecurity expands that scope to complex environments: multi-cloud, distributed identities, product security, vendor ecosystems, and global compliance. Enterprises must prove resilience at scale, integrate security into software delivery, and publish customer-facing evidence (Trust Centers, SOC 2/ISO reports). The difference is not just size; it’s the depth of governance, telemetry, and proof required to pass Fortune-grade procurement.
What are the 7 types of cybersecurity that enterprises must adopt?
- Network Security (segmentation, IDS/IPS)
- Endpoint Security (EDR, device posture)
- Identity & Access Management (SSO, MFA, JIT)
- Application Security (SAST/DAST, SBOMs)
- Cloud Security (CSPM/CIEM, key management)
- Data Security (DLP, encryption, classification)
- Security Operations & IR (SIEM, SOAR, playbooks)
Together they build layered defense. Map each type to business metrics—downtime avoidance, fraud reduction, audit speed—and you’ll tell a persuasive ROI story to executives and buyers.
What do you mean by enterprise security and why is it critical for Tier One companies?
Enterprise security is the system of controls protecting complex organizations—people, process, tech, and evidence. Tier One companies face higher stakes: brand impact, regulatory exposure, and global supplier obligations. They must show customers and regulators that breaches are unlikely, contained, and recoverable. Strong programs unlock market access, reduce premiums, and speed sales. In other words, enterprise security is table stakes for growth in the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia.
Which are the best enterprise cybersecurity courses in the USA, UK, and Canada?
Look for courses aligned to NIST/ISO, with hands-on labs and governance content: SANS enterprise tracks, ISC² CGRC/CISSP prep, ISACA CISM/COBIT courses, and university executive programs focused on GRC and cloud security. Prioritize curricula that include tabletop exercises, control mapping, and metrics. For managers, a short course in FAIR risk quantification helps translate security to finance language. Always check instructor credentials and alumni outcomes.
Top enterprise cybersecurity companies: Who delivers the best ROI and services?
“Best” depends on your stack and sector. Many enterprises blend platform vendors (identity, endpoint, cloud posture) with managed detection and advisory partners. ROI comes from integration quality, time to value, and outcome metrics (incidents avoided, MTTR, audit time saved). Ask for references in your industry and size band, insist on runbook transparency, and pilot against a clear success plan. The right partner reduces tool sprawl and proves impact within a quarter.
Enterprise cybersecurity salary guide: What do professionals earn in Tier One markets?
Ranges vary by role and region. In the USA, enterprise SOC leads and detection engineers often command six figures; CISOs are higher. In the UK, security architects and GRC managers are strong earners, especially in finance. Canada sees competitive pay for cloud security and IR roles; Australia continues to rise with cloud adoption. Upside depends on certs, demonstrated outcomes, and cross-functional leadership (risk, finance, legal).
What are the top enterprise cybersecurity books and PDFs for CISOs and IT leaders
Build a stack that spans strategy and practice: books on risk quantification (FAIR), Zero Trust, cloud security architecture, and incident response. Pair with PDFs from NIST (CSF, SP800 series), ISO 27001 guidance, CIS Controls, and your local privacy authority. The best resources help you implement and measure, not just conceptualize—favor works that include KPIs, playbooks, and case studies you can adapt.
Enterprise cybersecurity jobs 2025: Which roles are in highest demand in the USA and Australia?
Expect growth in cloud security engineering, detection engineering, identity governance, product security, and GRC automation. The USA market prizes hybrid engineers who can code detections and automate playbooks. Australia’s demand surges with cloud-first programs, incident response, and identity. For mobility, collect achievements, not titles: tuned a noisy detection, cut MTTR, passed a SOC 2 with zero major findings—these bullets travel internationally.
Enterprise cybersecurity framework comparison: NIST vs ISO for Tier One compliance
NIST CSF is a flexible maturity model favored in the US; ISO 27001 is a certifiable standard with global recognition. Many enterprises adopt NIST for internal roadmap governance and pursue ISO for an external badge. If you sell internationally, ISO helps bypass procurement friction; if you need board-friendly evolution stages, NIST shines. Best practice: map NIST to ISO and automate evidence so you can speak both languages.
Enterprise Cybersecurity Gatecha: Is it worth the investment for ROI and career growth?
Programs like Georgia Tech’s enterprise cyber offerings can be valuable for leaders needing depth in architecture, policy, and risk. Evaluate fit by reviewing syllabus, faculty, and capstones. If your role benefits from structured academic rigor and peer networks, the ROI can be strong—especially when employers sponsor. Pair academic work with real metrics at your job (e.g., control coverage, incident reductions) to translate coursework into promotion-ready outcomes.
Enterprise cybersecurity cost: How much should businesses budget for trust and conversions?
Budgets vary by sector and risk appetite, but many enterprises benchmark security spend as a % of IT revenue/cost. A practical approach: estimate annualized loss expectancy for your top risks, then fund controls that reduce expected loss and accelerate revenue (faster audits, better insurance terms, trust-driven conversion). Track savings from tool consolidation, reduced incidents, and shorter sales cycles. The right number is the one that pays for itself in avoiding loss and growth wins.
