Cybersecurity vs Computer Science 2025: Compare salaries, jobs, skills & ROI in the USA, UK, Canada & Australia. Choose the career that pays.
You’re choosing between two powerhouse paths—Cybersecurity and Computer Science—and the stakes feel high: tuition, time, and the promise of a career that pays well and stays relevant. Picture two grads starting in 2025. Maya majors in Cybersecurity, joins a managed security provider, and within 18 months moves from SOC Tier-1 to cloud security engineering. Liam majors in Computer Science, ships software at a fintech, and pivots into platform engineering as AI workloads scale. Both are winning stories—but the routes, ramp-up, and ROI differ.
In the U.S., software developers currently edge out cybersecurity analysts on median pay, while cybersecurity’s growth rate leads by a wide margin. In the UK, Canada, and Australia, pay bands overlap heavily by role and seniority, and specialized skills—cloud, AppSec, identity, DFIR—unlock bigger packages regardless of degree label. The ROI lens isn’t just “who earns more on day one.” It’s time-to-first offer, rate of salary growth, recession resilience, sponsorship options, and your ability to convert interviews into offers.
This guide breaks down the differences with real salaries, outlooks, course maps, and step-by-step decisions—so you can pick the path that maximizes your lifetime ROI and reduces risk. Key Tip: treat “Cybersecurity vs Computer Science” less like a rivalry and more like two overlapping highways—you can merge later via certificates, projects, or a focused master’s. Explore more details here → Role maps & skill stacks by market
| Factor | Cybersecurity Degree | Computer Science Degree |
| Focus | Defense, assurance, risk | Creation, optimization, scale |
| Labs | Blue team ranges, DFIR | OS/DB/compilers, distributed labs |
| Early Jobs | SOC, IR, IAM, GRC | SWE, QA, data eng, SRE |
| Best Add-on | DevOps/AppSec | Security minor/certs |
What is Cybersecurity? Enterprise Guide to Risk, ROI, and Growth
Cybersecurity protects systems, data, and people from threats that can halt operations, drain revenue, and damage trust. In practice, that means prevention (hardening & identity), detection (monitoring & threat intel), response (DFIR & crisis comms), and resilience (backup, recovery, and tabletop exercises).
Why enterprises invest (and you benefit):
- Attack frequency & impact: Security incidents create direct costs (ransom, downtime), indirect costs (brand damage), and regulatory exposure. Securing high-value data and regulated workloads (finance, healthcare, critical infrastructure) makes security talent non-optional.
- Revenue defense: Buyers want proof (SOC 2, ISO 27001). Security maturity becomes a sales enabler.
- AI & cloud velocity: New surfaces (LLMs, multi-cloud, SaaS sprawl) widen attack paths; orgs fund security to keep shipping safely.
Where Cyber shows ROI inside the business (and in your paycheck):
| Business Goal | Security Motion | Measurable Result |
| Faster audits | Evidence automation, control mapping | Shorter sales cycles, lower audit costs |
| Fewer incidents | Patch, identity, zero-trust, EDR | Reduced downtime, lower insurance |
| Customer trust | Compliance (SOC 2/ISO) & attestations | Higher conversion, bigger deals |
| Efficient Dev | AppSec/DevSecOps pipelines | Fewer late-stage defects, faster releases |
Mini case study: A UK SaaS vendor lost deals after a buyer asked for ISO evidence they didn’t have. After six months of risk mapping, logging, and controls, they won back the pipeline and shortened close times—security became a conversion engine.
Key Takeaway: Cybersecurity isn’t just a cost center; it’s risk-to-revenue alchemy. If you like puzzles, policy, and high-stakes teamwork, security’s a strong bet.
What’s the Difference Between Cybersecurity and Computer Science for Tier One Careers?
Computer Science (CS) is the broad foundation—algorithms, systems, networks, AI/ML, databases, distributed systems, and programming languages. Cybersecurity is a specialized slice focused on safeguarding those systems.
Day-to-day contrasts
- CS roles: Build and ship—applications, platforms, data pipelines, ML features. Success = user impact, performance, maintainability.
- Cyber roles: Defend and assure—threat hunting, incident response, identity & access, governance/risk/compliance, security architecture. Success = fewer incidents, faster response, provable controls.
Overlap: Both demand scripting, automation, networks, OS internals, and cloud fluency. Many engineers blend them (e.g., AppSec engineers embed in dev teams; security engineers write IaC and detectors).
Quick comparison
| Dimension | Computer Science | Cybersecurity |
| Primary Goal | Create software/systems | Protect software/systems & data |
| Early Roles | SWE, QA/Testing, Data Eng | SOC Analyst, IR, IAM, GRC |
| Tooling | Git, CI/CD, containers, DB, ML | EDR/SIEM, IAM, CSPM, SOAR, DLP |
| KPIs | Features shipped, latency, uptime | MTTD/MTTR, audit pass, risk reduction |
| Common Bridge | AppSec, Cloud Sec, SRE | AppSec, SecEng, SecOps |
Cybersecurity vs Computer Science: Salary, ROI, and Job Outlook in High-Demand Markets
United States (Median Pay & Outlook)
- Information Security Analysts: $124,910 median (May 2024); +29% job growth projected 2024–34.
- Software Developers: $133,080 median (May 2024); +15–16% job growth projected 2024–34.
UK (Typical Bands, 2025)
- Cybersecurity Analyst: common ranges £37k–£80k+ by experience; medians around the mid-40s to mid-50s depending on region and dataset.
- Software Developers: wide ranges by stack/region; London premiums apply (ONS ASHE datasets underpin going-rate policy).
Canada (Typical Bands)
- Cybersecurity Analyst: C$28.85–C$71.43/hour across regions (roughly C$60k–C$149k full-time equivalent).
- Software Developer: C$28.75–C$69.71/hour (roughly C$60k–C$145k).
Australia (Typical Bands)
- Cyber Security Analyst: A$105k–A$125k average; seniors higher.
- Software Developer: A$90k–A$110k average; seniors higher; city premiums.
Salary Snapshot (select roles, mid-career)
| Region | Cyber (Analyst/Engineer) | Software Developer/Engineer |
| USA | $125k median; growth +29% | $133k median; growth +15–16% |
| UK | ~£45k–£56k median (range wider in London) | Similar medians with London premiums |
| Canada | C$60k–C$149k (regional range) | C$60k–C$145k (regional range) |
| Australia | A$105k–A$140k typical | A$90k–A$130k typical |
Result: In the U.S., devs often start higher on median pay, but cybersecurity wins on growth velocity. In the UK/Canada/Australia, the spread overlaps; specialization (cloud/AppSec/IAM) and employer size move the needle most. Explore more details here → Target a role, then align certs/projects to that role’s tools.
Are Degrees in Cybersecurity and Computer Science Worth It for Long-Term Career Growth?
Short answer: Yes—if you align the degree with hands-on projects, internships, and stackable credentials. The degree opens doors; the portfolio converts offers.
Cost & ROI (annual sticker price, typical)
| Country | Typical Public/“Home” Tuition (UG) | Notes |
| USA | Public in-state ≈ $11,610; Private ≈ $43,350 (2024–25 averages) | Sticker price; aid varies. |
| UK (England) | Cap rising to £9,535 in 2025–26 | Inflation-linked increase. |
| Canada | Varies by province; see StatsCan 2024–25 | Field-specific fees differ. |
| Australia | CSP student contributions (discipline-based, indexed annually) | HECS-HELP available. |
Path to value:
- Intern early (SOC, IT, research lab, or dev team).
- Publish work (GitHub, writeups, capture-the-flag, open-source issues).
- Certs tactically: one signal-boosting cert beats five vague badges.
- Mentors: pair with a senior in your target sub-domain.
- Geo/remote strategy: target markets with higher density (London, NYC, Toronto, Sydney) or remote-first employers.
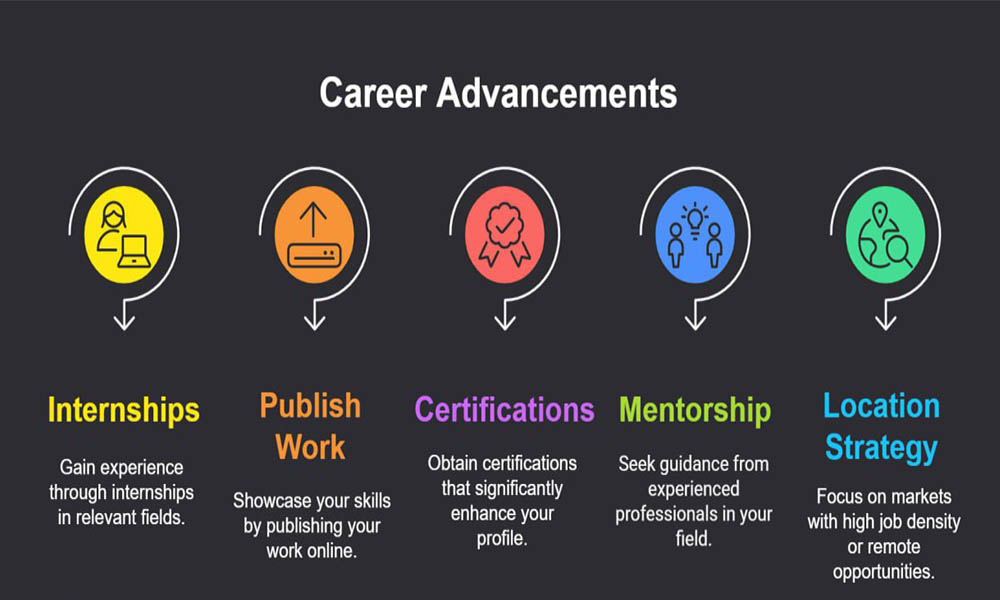
Takeaway: Degrees pay off fastest when you ship evidence (projects) and stack skills that map to well-funded problems (cloud, identity, AppSec, AI safety).
Cybersecurity vs Computer Science Careers: Which Path Offers Higher ROI and Conversion?
Think of Conversion as your odds of landing interviews and offers. Cyber offers high conversion into entry roles via SOC, IT security, and GRC apprenticeships. CS offers high conversion through internships and new-grad pipelines—especially if you can demo projects or internships at brand-name firms.
Pros/cons for ROI
| Path | ROI Pros | ROI Cons |
| Cybersecurity | Strong demand, regulated buyers, diverse entry points (SOC/GRC) | On-call/incident stress, tool sprawl, audits |
| Computer Science | Broad roles, strong ceiling (SWE/ML/SRE), product impact | Higher bar for entry at elite firms; interview rigor |
Expert insight: In the U.S., security roles grow faster than dev overall; in bad markets, cyber hiring often slows less. In roaring markets, dev comp can surge faster (equity/bonus). Balance growth rate vs comp ceiling—and pick where you’ll excel.
Key Result: Choose the stream where you can show signal fast—then specialize to increase comp.
Specializations in Cybersecurity That Drive Enterprise Trust and Lead Generation
High-impact, high-budget niches:
- Cloud Security (AWS/Azure/GCP): IaC guardrails, identity boundaries, workload isolation.
- AppSec/DevSecOps: SAST/DAST/IAST, threat modeling, SDLC policies; partners tightly with dev teams.
- Identity & Access (IAM/PAM/IGA): Least privilege at scale; often tied to compliance wins.
- DFIR/Threat Hunting: Detection engineering, log pipelines, purple teaming.
- GRC & Compliance: Framework mapping (SOC 2, ISO 27001), evidence collection.
- OT/ICS Security: Manufacturing, energy, utilities—safety meets security.
- AI/Model Security: Prompt injection defenses, model governance, data loss controls.
Table: Specialization signals
| Specialization | Proof of Skill |
| Cloud Sec | Secure IaC repo; misconfig detectors; multi-account baseline |
| AppSec | Fix PRs, create secure coding linters, threat models |
| DFIR | Home lab, attack chains, detection rules with tests |
| GRC | Control matrix, audit evidence runbooks, policy-as-code |
| IAM | JIT access workflows, policy simulation, break-glass tests |
Expert Takeaway: Roles closest to revenue and audits (cloud, AppSec, IAM, GRC) tend to get funded first.
Key Differences Between Cybersecurity and Computer Science Degrees Explained
Cybersecurity degree modules often include:
- Security fundamentals, network security, cryptography
- Secure systems, incident response, malware analysis
- Risk management, privacy law, governance
Computer Science degree modules often include:
- Algorithms, data structures, programming languages
- Operating systems, networks, databases
- Distributed systems, AI/ML, compilers
Comparison
Insight: Either path can reach Security Engineer, AppSec, or SRE—bridge with projects.
Major Similarities Between Cybersecurity and Computer Science for Enterprise IT Teams
Both tracks value:
- Systems thinking: OS internals, networks, distributed systems
- Automation: Python/Bash, IaC, CI/CD
- Cloud fluency: IAM, VPC, containers, serverless
- Data: Logging, metrics, telemetry
Skills Matrix
| Skill | CS | Cyber |
| Python scripting | ✅ | ✅ |
| Linux/Networking | ✅ | ✅ |
| Cloud IAM | ⚪️ | ✅ |
| Algorithms/DS | ✅ | ⚪️ |
| Threat modeling | ⚪️ | ✅ |
| Observability | ✅ | ✅ |
Takeaway: Shared foundations make switching feasible—that’s your safety net.
Cybersecurity vs Computer Science: Which Degree is Right for Me in Tier One Countries?
- If you love building & product velocity → CS. Stack DevOps, distributed systems, and a security minor to stay resilient.
- If you love defending & governing → Cyber. Stack cloud, identity, and AppSec to widen options.
- If uncertain → Start CS core, choose security-heavy electives, do a security internship, then commit.
Key Tip: Match your market. U.S. offers high comp and steep interview ladders; UK has strong compliance-led demand; Canada values bilingual and public-sector security; Australia pays well for cloud & identity.
Result: Pick the track that keeps you motivated—because velocity compounds ROI.
Typical Computer Science Courses Explained for ROI-Focused Learners
- Algorithms & Data Structures: Ace interviews; write efficient code under constraints.
- Operating Systems: Understand processes, memory, concurrency—great for SRE/security.
- Networks: Protocols, routing, latency—vital for performance and defense.
- Databases: Query planning, indexing—feeds backend/data engineering.
- Distributed Systems: Consensus, sharding, failure modes—modern platform backbone.
- AI/ML: Model lifecycle; useful for data/AI roles and even security detection tuning.
Checklist to convert learning into offers
- Ship 3 portfolio projects (web, systems, data).
- Contribute to open source (1 bug fix/month).
- Internships or research every summer.
- Practice interview loops (DSA + systems design).
- Add one cloud cert to signal deploy-ready skills.
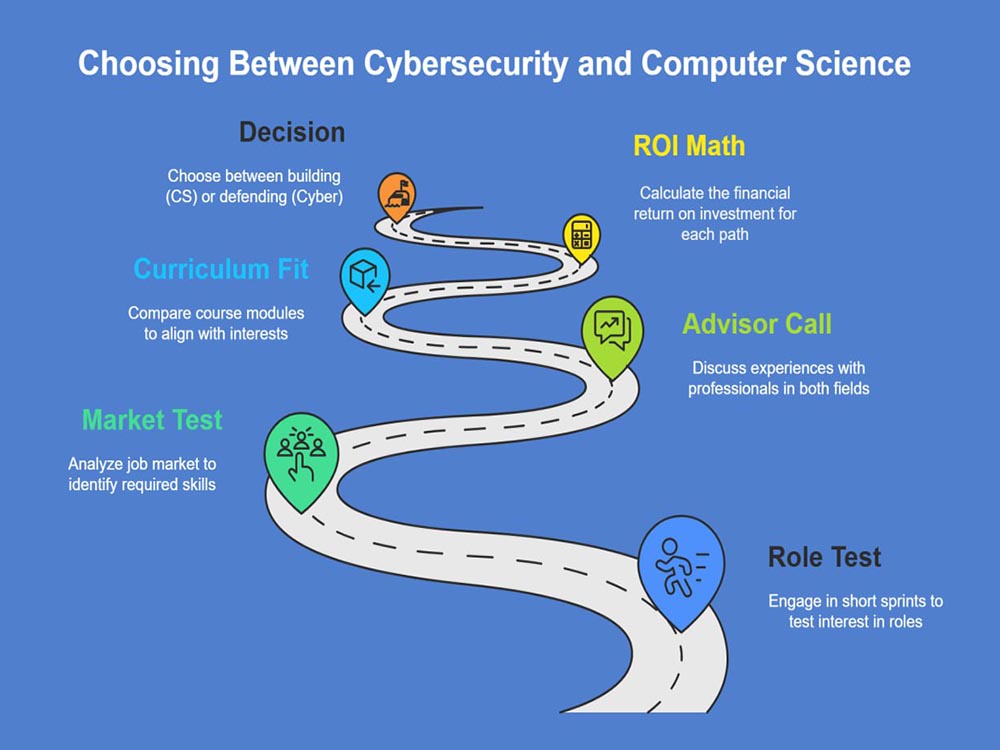
Should You Pursue a Cybersecurity or Computer Science Degree? Step-by-Step Decision Guide
- Role test: Do three short sprints—(a) build a small web service, (b) run a home SOC lab, (c) threat-model your project. Which was fun?
- Market test: Search 20 roles in your target city; tally skills required.
- Advisor call: Talk to one SWE and one Security Engineer about their week.
- Curriculum fit: Compare modules—do you prefer crypto & IR, or compilers & dist-sys?
- ROI math: Tuition × years + living costs − expected intern income.
- Decision: Choose build (CS) or defend (Cyber). Set a 12-month plan.
Computer Science vs Cyber Security: Enterprise Growth and Market Demand Comparison
U.S. snapshot: Security roles grow faster (+29% vs +15–16%), developers hold a higher median. Both outpace the average occupation by a lot.
UK/Canada/Australia: Security demand is amplified by compliance and cloud migration; developer demand spikes with AI and data platform build-outs. Expect frequent overlap in job posts (DevSecOps, AppSec). Result: The best hedge is cloud + automation with either degree.
Mini Table—What Funds First?
| Budget Driver | Hires Trend |
| Audit deadlines (SOC 2/ISO) | GRC, IAM, Cloud Sec |
| New product launches | SWE, SRE, AppSec |
| Breach/near-miss | DFIR, SecEng, detection |
Takeaway: Follow the budget drivers to ride hiring waves.
Cybersecurity vs Computer Science Skills Comparison for High-Paying Jobs in the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia
| Category | High-ROI Skills |
| Universal | Python, Git, Linux, cloud basics, SQL, Terraform |
| CS-leaning | Distributed systems, data engineering, MLops, performance tuning |
| Cyber-leaning | IAM policy, EDR/SIEM, threat hunting, AppSec, incident response |
| Both benefit from | Systems design, observability, cost-aware architecture |
Key Tip: The strongest profiles show depth in one and literacy in the other.
Cybersecurity Certifications: Best ROI-Driven Credentials for Tier One Professionals
- Entry/early: Security+, SSCP (broad base), AZ-900/AWS CCP (cloud literacy)
- Mid: CySA+, CEH (for pen-testing tracks), GIAC GSEC/GCIH/GCIA (if budget allows)
- Senior: CISSP, CISM (leadership/GRC), CCSK/CCSP (cloud), OSCP (hands-on offensive)
- Cloud security: AWS Security Specialty, Azure Security Engineer, Google Professional Cloud Security Engineer
Pro Tip: Map certs to job descriptions you want—then earn only those that move your short-term conversion.
Computer Science Certifications: Career Growth and Salary Insights in USA & UK
CS careers don’t rely on certs, but vendor/platform badges help:
- Cloud: AWS Solutions Architect, Azure Administrator/Engineer, Google Professional Cloud Architect
- Containers: CKA/CKAD
- Data: Databricks, Snowflake, dbt
- Language/stack: Java (Oracle), .NET (MS), front-end frameworks (course certs)
Use them to signal deploy-ready skills and unlock interviews, especially in UK/EU markets that prize “proof” of platform know-how.
Case Study: Computer and Information Research Scientist Roles in Global Enterprises
These roles research new algorithms, ML methods, or systems designs—often in R&D labs or advanced product teams. In the U.S., median pay sits around $140k with ~20% projected growth through 2034, and most roles expect a master’s degree or PhD (some federal roles accept a bachelor’s).
Takeaway: If you love mathy CS and research, this path pays well but needs deeper academics.
U.S.: Both tracks win—security grows faster; devs command high medians and massive ceilings at big tech.
UK: Security pay rises track identity/AppSec/cloud; developer compensation spikes in fintech and AI roles.
Canada: Provincial differences matter; public-sector and finance drive cyber; product firms and SaaS drive dev. Australia: Strong pay for both; cloud/IAM/AppSec and high-growth tech hubs set premiums.
Bottom line: Pick the funded problem in your region; specialize to ride the updraft.
‘‘Which One is Better, Computer Science or Cyber Security? Expert Insights 2025
Neither wins universally. If you want highest growth odds and love defense, choose Cybersecurity. If you want highest compensation ceiling and love building, choose CS/SWE. In the U.S., software dev median pay is higher; security grows faster. In other Tier One markets, ranges overlap heavily; specialization and employer quality matter more than the degree label.
Takeaway: Choose the path you’ll stick with and accelerate—that’s where ROI compounds.“Is Cyber Security Better Than Coding for ROI and Career Conversion?
Cyber often has lower barriers to first security role (SOC/GRC pathways, apprenticeships) and high demand from compliance-driven buyers. Coding (SWE) can deliver higher comp ceilings, especially at scale or with equity. Many pros blend both: AppSec engineers, security-minded SREs, or detection engineers who code. Result: The best ROI comes from coding + security in one profile.
Is Cyber Security Under IT or Computer Science? Academic and Industry Views
Academically, cybersecurity is typically housed under Computer Science, Information Security, or Information Systems. In industry, it touches IT operations, engineering, and risk/compliance. Expect to collaborate across departments—CS fundamentals + IT execution + GRC rigor. That mix is why security talent stays in demand.
Who Gets Paid More: Cyber Security Specialist or Software Engineer in Tier One Countries?”
U.S. medians: Software developers edge higher; security analysts are close behind but grow faster. UK/Canada/Australia: Spread overlaps; senior security engineers, architects, and managers can out-earn many devs, while principal/staff engineers in CS can leapfrog most roles. Your specialization and employer matter more than the banner.
FAQs:
Cybersecurity vs Computer Science salary: Which degree offers the highest ROI in the USA and UK?
U.S.: software developers hold a slightly higher median pay (≈$133k) than information security analysts (≈$125k), while security grows faster (+29% vs +15–16%). UK: medians overlap widely; many cyber analysts report mid-40s to mid-50s (£k) with London premiums; experienced security architects and AppSec engineers can surpass typical dev bands. ROI depends on specialization and employer quality.
Cybersecurity vs Computer Science jobs: Which path offers more Tier One career growth opportunities?
Both expand rapidly. Security demand is powered by regulation and cloud adoption; dev demand is powered by AI/data and product velocity. In the U.S., security growth is projected at +29% (2024–34), while software dev is +15–16%—both “much faster than average.” Choose the stream you’ll excel in, then add the other as a minor.
What is harder, Computer Science or Cyber Security, for students in Canada and Australia?
“Hard” is personal. CS leans theoretical (algorithms, systems), while Cyber blends technical depth with policy and incident pressure. In Canada and Australia, both fields expect coding and cloud literacy; Cyber adds on-call/incident stress, while CS interviews can be intense (DSA/system design). Pick based on what you enjoy doing weekly—that’s the true difficulty filter.
Cybersecurity vs Computer Science Reddit: What do real professionals say about ROI and salaries?
Common themes: (1) Strong CS fundamentals help in both careers, (2) Cyber’s entry paths are accessible via SOC/GRC + certs, (3) Highest comp often pairs CS depth + security specialization (AppSec, SecEng, SRE). Treat Reddit as anecdotal; validate with official stats and local job data.
Cybersecurity vs Computer Science Masters: Which graduate program provides better job conversion?
If you’re switching from non-CS, an MS in CS can unlock SWE/data roles across industries. If you’re already technical, an MS in Cybersecurity or Information Security accelerates into SecEng, AppSec, IAM, or GRC leadership. Conversion is strongest when you ship projects, secure internships, and align capstone work with hiring teams’ stacks.
Is Cyber Security under Computer Science or Computer Engineering in Tier One universities?
Often under Computer Science or a dedicated Information Security school; some programs live in Engineering (Computer or Electrical) or Information schools. The banner matters less than course content and lab access (cloud, DFIR ranges, AppSec). Check modules and industry placements.
Cybersecurity vs Computer Science salary Reddit: Real salary reports from professionals in 2025
Anecdotes vary. U.S. reports often show six-figure SWE comp with higher ceilings; security engineers and architects also clear six figures, with faster role growth. UK/Canada/Australia threads echo wide ranges and city premiums. Use community data as directional, but anchor decisions to BLS/ONS/StatsCan and local offers.
Best Computer Science and Cyber Security colleges in USA, UK, Canada, and Australia
“Best” depends on fit: research output, co-ops/internships, industry partners, and lab resources. In the UK, consult league tables and accreditation; note the 2026 guide trends and financial pressures as context, not destiny. In North America and Australia, prioritize programs with strong industry pipelines and cloud/security labs.
Cybersecurity vs Computer Science comparison checklist: Skills, salary, and ROI explained
Use this quick checklist: (1) Pick build or defend, (2) Map 10 target job posts’ skills, (3) Choose degree path, (4) Add 1–2 certs that match those posts, (5) Build a 3-project portfolio, (6) Intern every summer, (7) Track comp using official sources each year (BLS/ONS/StatsCan).
Cybersecurity vs Computer Science services: Which degree leads to more enterprise consulting opportunities?
Both. Cyber consulting (GRC, cloud security, IR readiness) is evergreen—especially in regulated sectors. CS consulting thrives in data/AI platforms, migrations, and performance engineering. If you want client-facing work fast, Cyber + compliance frameworks often wins; if you want product builds, CS + cloud data engineering soars.
Top Cybersecurity vs Computer Science careers with highest lead generation potential in 2025
- Cyber: Cloud Security Architect, IAM Engineer, AppSec Engineer, DFIR Lead, GRC Lead.
- CS: Staff/Principal SWE, SRE, Data/ML Engineer, Platform Engineer.
Roles tied to compliance deadlines or AI platform launches generate the most inbound interest.
Cybersecurity vs Computer Science cost of education: Which degree offers better ROI in Tier One countries?
Costs are similar by institution; ROI depends on speed to internship and specialization. Benchmarks: U.S. public in-state ≈ $11.6k/yr, private ≈ $43k/yr; UK home fee cap £9,535 (2025–26); Canada varies by province/field; Australia uses CSP student contributions by discipline. Offset costs with internships, co-ops, scholarships, and employer sponsorships.