Boost ROI with cybersecurity monitoring—uptime, compliance, sales. See SIEM tools, checklists & case studies.
Cybersecurity monitoring is no longer a “nice to have.” It’s a growth engine. In Tier One markets—the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia—buyers scan security signals before they ever book a demo or sign a PO. They check if your site uses HTTPS; they look for SOC 2 and ISO 27001 badges; they skim breach headlines. One missed alert or slow response erodes trust and drags down conversions across your entire funnel.
This guide shows how modern enterprises turn continuous monitoring into measurable ROI: lower risk, faster sales cycles, higher win rates, and stronger lifetime value. We unpack what to monitor (identity, endpoints, cloud, network, apps, data), which metrics matter (MTTD, MTTR, coverage, signal-to-noise), and how to embed monitoring into DevSecOps without slowing delivery. You’ll see mini case studies, simple checklists, and side-by-side tables for tools and workflows.
Key promise: when you align cybersecurity monitoring with customer-facing outcomes—uptime, privacy, compliance—you defend revenue, not just infrastructure. You shorten vendor due diligence, pass audits faster, and keep digital experiences reliable. This is how security becomes a growth multiplier for CIOs and CTOs who sell into compliance-heavy sectors in the US, UK, Canada, and Australia.
Key Tip: Tie every monitoring objective to a revenue or retention KPI.
Result: Security stops being a cost center and starts earning stakeholder trust.
Explore more details here → Build a one-page “Security ROI” dashboard for execs.
What is Cybersecurity Monitoring? Complete Overview for CIOs & CTOs
Cybersecurity monitoring is the continuous collection, correlation, and analysis of security-relevant data across your attack surface—users, devices, networks, applications, cloud services, and third-party integrations. The goal is simple: detect, investigate, and respond to threats before they become incidents that harm customers, revenue, or brand.
Core components:
- Telemetry: Logs, metrics, traces, alerts from SIEM, EDR/XDR, CSPM, IAM, WAF, API gateways, data stores.
- Analytics: Rules, detections, threat intel, ML models to find anomalies and reduce noise.
- Response: Playbooks, automation (SOAR), and human analysts to contain and eradicate threats.
- Governance: Evidence for audits (SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS), risk registers, and KPIs.
Why it matters for growth: Buyers in Tier One markets must prove due diligence. Your monitoring program supplies the real-time evidence that satisfies procurement, slashes vendor risk questionnaires, and accelerates closings.
Mini Case Study (UK Fintech): A payments firm mapped monitoring KPIs (MTTD < 10 min, MTTR < 60 min) to SLA credits. Sales cycles dropped by 18% because procurement trusted the firm’s live metrics.
Monitoring Landscape (at a glance)
| Layer | What to Watch | Signal Examples | Typical Tools |
| Identity (IAM) | Privileged access, MFA drift, stale accounts | Impossible travel, MFA disabled | Entra/Microsoft, Okta, Ping |
| Endpoint/Workload | Malware, EDR signals, kernel events | Ransomware patterns, lateral movement | CrowdStrike, SentinelOne, Defender |
| Network | East–west traffic, DNS, egress | Beaconing, DGA domains | NetFlow, Zeek, IDS/IPS |
| Cloud/SaaS | Misconfig, CSPM drift, API abuse | Public S3, over-broad roles | Wiz, Prisma, Lacework |
| App/API | Auth bypass, injection, bot abuse | 4xx/5xx spikes, token misuse | WAF, RASP, API gateways |
| Data | DLP, encryption, access | Exfil to unsanctioned apps | DLP, DSPM |
Takeaway: Monitoring is a system. Design for coverage, quality, and response—not just more data.
Steps for Implementing Cybersecurity Monitoring to Drive ROI for Enterprises
Step 1 — Define business outcomes. Map monitoring to revenue, uptime, and compliance. Example: “Reduce MTTR from 4 hours to 45 minutes to protect checkout reliability.”
Step 2 — Inventory the attack surface. Catalog assets, data flows, crown jewels, and third parties (including AI and SaaS). Prioritize by business impact.
Step 3 — Instrument telemetry. Standardize log schemas and retention. Ensure identity, endpoint, cloud, and app telemetry flow into your SIEM/XDR.
Step 4 — Write detections that matter. Focus on top misuse cases: credential abuse, privilege escalation, suspicious egress, data exfiltration, and supply chain anomalies.
Step 5 — Automate tier-1 response. SOAR playbooks should isolate hosts, rotate credentials, block tokens, and open tickets with context.
Step 6 — Prove compliance early. Tag evidence to controls (SOC 2, ISO 27001, GDPR). Pre-answer vendor questionnaires with monitoring artifacts.
Step 7 — Review and tune monthly. Retire noisy rules, add high-fidelity detections, test runbooks.
Implementation Roadmap (first 90 days)
| Phase | Days | Outcome | KPI |
| Sprint 0 | 0–7 | Scope, KPIs, exec sign-off | KPI deck |
| Sprint 1 | 8–30 | Telemetry baseline, critical detections | Coverage % |
| Sprint 2 | 31–60 | SOAR playbooks live | Auto-close rate |
| Sprint 3 | 61–90 | Compliance evidence mapped | Audit readiness score |
Result: Sales cycles shrink 10–25% when you supply live monitoring KPIs during due diligence.
Challenges in Cybersecurity Monitoring for Tier One Businesses & How to Overcome Them
Noise & fatigue: Too many alerts bury the real ones.
Fix: Create a “Top 20 Detections” list linked to the kill chain. Measure signal-to-noise weekly.
Tool overlap: Redundant tools inflate costs and complicate response.
Fix: Consolidate where possible (XDR + Cloud-native) and define clear handoffs.
Cloud and SaaS drift: Constant change breaks rules and visibility.
Fix: Use IaC guardrails and continuous posture checks (CSPM/DSPM).
Talent shortage: SOC burnout strains coverage.
Fix: Automate tier-1/2 tasks; partner with MDR for 24×7 without exploding headcount.
Board alignment: Security KPIs feel abstract.
Fix: Translate into revenue protection: “minutes of customer-impacting risk avoided.”
Challenge Matrix
| Challenge | Risk | Countermeasure | ROI Lever |
| Noise | Missed incidents | Top 20 detections, QA | Fewer breaches |
| Tool overlap | Cost bloat | Consolidation | Lower TCO |
| Drift | Misconfig breaches | IaC + CSPM | Audit wins |
| Burnout | Coverage gaps | SOAR + MDR | 24×7 defense |
| Board gaps | Budget cuts | KPI-to-revenue | Faster sales |
Takeaway: You don’t need more alerts; you need better ones.
Best Practices in Cybersecurity Monitoring to Build Trust and Conversions
- Identity-first: Monitor privileged access and token misuse first.
- Detections-as-code: Version, review, and test rules like software.
- Mean Time to… Everything: Track MTTD, MTTR, and “time to business impact avoided.”
- Close the loop: Every high-severity alert must end with a control improvement.
- Customer-facing trust: Publish uptime, status history, and compliance scope.
- Tabletop quarterly: Test your response with real data and executive participation.
- Evidence tagging: Auto-attach logs and artifacts to controls for audits.

Practice-to-Outcome Map
| Practice | Metric | Business Impact |
| Identity-first | Phishing success rate ↓ | Fewer account takeovers |
| Detections-as-code | False positives ↓ | Analyst time reclaimed |
| SOAR playbooks | MTTR ↓ | Less downtime |
| Trust Center | Win rate ↑ | Shorter sales cycles |
Key Tip: Measure “alerts closed by automation.”
Result: You scale defense without scaling headcount.
Explore more details here → Add 3 automation playbooks per quarter.
Importance of Cybersecurity Monitoring in Enterprise Risk Reduction & Growth
A strong monitoring program does three things: reduces the chance of a material incident, shrinks the impact window when one occurs, and proves trust to buyers and regulators. That combination drives growth in Tier One markets where vendor scrutiny is high.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons (and Mitigations) |
| Faster incident containment | Upfront integration effort → phase by system |
| Audit-ready evidence | Alert fatigue → “Top 20” rule set |
| Shorter sales cycles | Skills gap → MDR + automation |
| Better SLOs & uptime | Tool sprawl → platform consolidation |
Expert Insight: The most mature programs invest first in identity, then data, then everything else. Attackers pivot fastest through identity.
Cyber Essentials Checklist: Essential Monitoring Steps for Business Continuity
Checklist (start here):
- MFA enforced; admin accounts reviewed weekly.
- EDR/XDR deployed to 100% of endpoints and cloud workloads.
- SIEM/XDR receiving logs from IAM, EDR, cloud, WAF, and critical apps.
- Detections for credential abuse, lateral movement, unusual egress, and data exfil.
- SOAR playbooks for isolate host, disable token, rotate keys, block domain.
- CSPM and DSPM scanning daily; critical misconfigs remediated within 24–72 hours.
- Immutable backups and tested restores (RPO/RTO defined).
- Vendor monitoring: high-risk SaaS and IDP logs ingested.
- Evidence mapped to SOC 2/ISO controls.
Quick Comparison
| Item | Minimum | Mature |
| Identity | MFA + Just-In-Time | Continuous session analytics |
| Endpoints | EDR everywhere | XDR + automated isolation |
| Cloud | Basic CSPM | IaC + policy-as-code |
| Response | Manual tickets | SOAR + auto-remediation |
Takeaway: Business continuity depends on disciplined basics.
DevSecOps & Cybersecurity Monitoring: Benefits, Challenges, and ROI for Enterprises
Benefits: Earlier detection, fewer hotfixes, faster audits. Shift-left logging and runtime policies catch issues before production.
Challenges: Pipeline noise, developer friction, and competing priorities.
ROI: Fewer incidents after release, faster mean time to recovery, and better change success rates.
DevSecOps Monitoring Map
| Stage | What to Monitor | Tooling Examples |
| Plan/Code | Secrets, dependency risks | SAST, SCA |
| Build | Image integrity, SBOM | CI scanners, attestations |
| Deploy | Config drift, IaC controls | Policy-as-code |
| Run | Runtime anomalies | EDR/XDR, RASP, WAF |
| Prove | Evidence to controls | GRC platforms |
Expert Insight: Treat detections as versioned code with tests. Roll them out through the same CI/CD you use for applications.
Top Compliance Automation Tools to Enhance Cybersecurity Monitoring Efficiency
Compliance automation aligns monitoring evidence with controls and auditor expectations. It reduces manual screenshots, maintains control mapping, and accelerates renewals.
Common Platforms (examples): Drata, Vanta, Secureframe, Hyperproof, AuditBoard, Strike Graph.
Where they help: Evidence collection (logs, configs), vendor risk workflows, continuous control monitoring, and policy attestations.
Selection Comparison
| Need | Good Fit | Why |
| Fast SOC 2 lift | Drata/Vanta | Broad integrations, quick wins |
| Multi-framework | Hyperproof/Secureframe | Flexible mapping across ISO, PCI, HIPAA |
| Audit workflow depth | AuditBoard | Strong GRC and audit lifecycle |
| Startup to mid-market | Strike Graph | Lean, scalable approach |
Takeaway: Let the platform gather evidence so your SOC can focus on detections and response.
Micro-CTA: Map your top 15 controls to automated evidence in 30 days.
How Network Monitoring Strengthens Cybersecurity for Global Enterprises
Network telemetry remains a high-signal source. Flow logs, DNS queries, and egress rules reveal command-and-control, exfiltration, and insider misuse. In hybrid environments across the US, UK, Canada, and Australia, consistent network monitoring policies bridge data centers, cloud VPCs/VNETs, and branch offices.
Checklist:
- Capture NetFlow/VPC Flow Logs; baseline normal east–west patterns.
- Inspect DNS for DGA domains and newly observed domains.
- Tag egress traffic from sensitive subnets; alert on unsanctioned destinations.
- Mirror traffic for IDS/IPS at critical choke points.
- Use TLS inspection where lawful; log JA3/JA4 fingerprints.
Incident Response Methodology: Engineering-Led Guide to Faster ROI
Prepare → Detect → Analyze → Contain → Eradicate → Recover → Learn. Tie each step to metrics and automation.
Engineering-led moves:
- Golden playbooks: Pre-approved isolation and key rotation.
- Live runbooks: ChatOps to trigger SOAR actions and track artifacts.
- Post-incident sprints: Convert lessons into PRs, rules, and IaC fixes.
KPIs: Mean time to contain, mean time to eradicate, and customer-impacting minutes avoided.
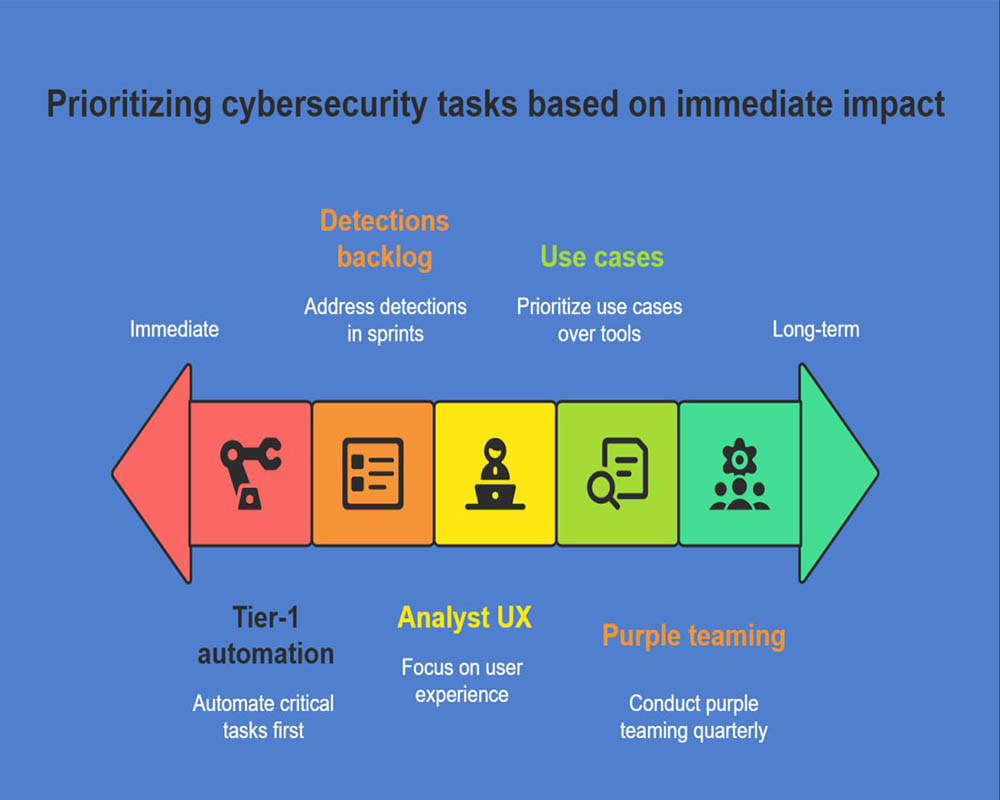
Top 5 SOC Best Practices to Overcome Modern Cybersecurity Monitoring Challenges
- Tier-1 automation first.
- Detections backlog with sprints.
- Purple teaming quarterly.
- Use cases over tools.
- Analyst UX matters.
SOC Maturity Snapshot
| Practice | Emerging | Advanced |
| Automation | Enrichment | Containment |
| Detections | Ad hoc | Versioned & tested |
| Hunt | Reactive | Hypothesis-driven |
| Reporting | Alerts count | Business impact |
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Enterprise Compliance ROI
A SIEM correlates logs and detections across your estate and anchors your evidence for audits. The ROI comes from centralized analytics, faster investigations, and compliance-ready reporting.
ROI Levers:
- Consolidation: Fewer consoles, faster queries.
- Automation: Auto-close benign alerts, pre-build incidents with context.
- Compliance: Map events to controls; export evidence on demand.
Practical Tips:
- Right-size ingestion; keep hot vs. cold storage tiers.
- Normalize schemas (e.g., ECS-like) for content reuse.
- Build 10 high-fidelity detections before adding long-tail rules.
Why Leading Enterprises Trust Cybersecurity Monitoring Services Worldwide
Enterprises in the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia rely on managed detection and response (MDR) and co-managed SOCs for 24×7 coverage, surge capacity, and specialized threat intel. Service partners bring content libraries, playbooks, and regional compliance expertise.
Benefits:
- Always-on monitoring without hiring delays.
- Benchmarked detections from multiple client environments.
- Faster audit prep with packaged evidence.
Case Study: Building a Proactive Cybersecurity Monitoring Strategy for Tier One Businesses
Context: A SaaS vendor serving UK healthcare and US finance faced long vendor risk reviews and rising alert fatigue.
Actions: Consolidated EDR+XDR, normalized logs to SIEM, built 18 high-fidelity detections, automated token revocation, and mapped evidence to SOC 2 + ISO.
Outcomes (6 months):
- MTTD: 22 → 6 minutes.
- MTTR: 190 → 47 minutes.
- Sales cycle: −14% due to a public Trust Center.
- Analyst capacity: +30% via auto-enrichment and isolation.
Tiny Table
| KPI | Before | After |
| MTTD | 22m | 6m |
| MTTR | 190m | 47m |
| Win rate | +0% | +8% |
Takeaway: Proactive monitoring fuels sales, not just security.
Key Security Monitoring Challenges Organizations Face in the USA & UK
- Complex regulatory overlap (state laws, GDPR/UK GDPR).
- Legacy systems and on-prem identities.
- Talent competition in major hubs.
What Works:
- Identity-first controls with privileged access reviews.
- Policy-as-code for cloud; CSPM + DSPM for data lineage.
- Co-managed SOC to cover nights/weekends.
Mini-Table
| Challenge | Quick Win |
| Legacy auth | MFA + conditional access |
| Data residency | Region-aware logging |
| Vendor reviews | Trust Center + evidence pack |
Enhancing SOC Efficiency with Cybersecurity Monitoring in Canada & Australia
Regional realities—data residency in Canada, sector-specific rules in Australia—mean your SOC needs clear boundaries and automation.
Moves that matter:
- Keep sensitive logs in-region; use federated queries.
- Automate isolation for endpoints and cloud roles.
- Add “instant comms” macros (legal, PR, execs) in incidents.
Impact: Better analyst focus, faster reports for regulators, fewer “all hands” escalations.
What is Monitoring in Security? Expert Insights for Tier One Enterprises
Security monitoring means continuously watching systems and identities to catch threats early. The expert twist: define “early” by business impact, not clock time. If you stop a credential attack before it reaches customer data, you won—even if it took 20 minutes.
Essentials:
- Identity and egress are your highest-signal lenses.
- Detections-as-code yields quality and reuse.
- Automation must be safe by design (guardrails + approvals).
Takeaway: Monitoring is an operating discipline that protects revenue as much as it protects infrastructure.
What is Cyber Threat Monitoring? ROI-Focused Guide for Decision-Makers
Cyber threat monitoring adds external intelligence—adversary TTPs, indicators, sector alerts—to your internal signals. It boosts context and elevates fidelity.
For decision-makers:
- Track threats that target your sector.
- Pre-build playbooks for top TTPs.
- Convert threat intel into detections and tabletop scenarios.
Result: Better prioritization, fewer false positives, and faster executive decisions during incidents.
What is Monitoring-as-a-Service in Cybersecurity? Cost & Growth Benefits
Monitoring-as-a-Service (MaaS) delivers 24×7 SOC coverage, detections, and response via a partner. You pay a subscription rather than staffing your own shifts.
Growth benefits: Faster compliance, shorter procurement timelines, and reliable customer SLAs.
Cost notes: Pricing varies by data volume, endpoints, and response scope. MaaS often lowers total cost versus hiring, especially for global coverage.
Takeaway: MaaS accelerates maturity without slowing your roadmap.
What is a Security Monitoring System? Enterprise-Grade Framework Explained
A security monitoring system combines telemetry (what you see), analytics (how you decide), and response (what you do). It must integrate identity, endpoint, cloud, network, app, and data signals, then drive consistent actions through SOAR and tickets.
Framework:
- Observe: Collect normalized logs/metrics/traces.
- Orient: Apply detections, intel, and baselines.
- Decide: Rank by business impact.
- Act: Automate safe responses; escalate with context.
Bottom line: A system that acts quickly—safely—pays for itself in avoided downtime and accelerated trust.
FAQs:
What are the best cybersecurity monitoring tools for enterprises in 2025?
Start with a platform core: SIEM (e.g., Splunk, Microsoft Sentinel, Google Chronicle, IBM QRadar, Elastic) plus XDR/EDR (e.g., CrowdStrike, Microsoft Defender, SentinelOne). Add cloud posture (Wiz, Prisma Cloud), identity analytics (Okta/Entra, Ping), WAF/API protection, and GRC/compliance automation (Drata, Vanta, Hyperproof). Choose tools that integrate well, export evidence, and support detections-as-code. Favor high-fidelity rules over giant rule sets, and make automation safe-by-default with approvals. Pilot with your top 10 detections before you scale.
How much does cybersecurity monitoring cost for businesses in the USA and UK?
Costs vary by data volume, seats, coverage hours, and response scope. SMBs often spend $2k–$10k/month for core SIEM/XDR with MDR. Mid-market programs range $10k–$40k/month with SOAR and cloud posture. Large enterprises spend $40k–$150k+/month depending on ingestion, regions, and 24×7 response. Include storage tiers (hot vs. cold), marketplace discounts, and personnel. ROI improves when you consolidate tools, automate tier-1, and map evidence to audits to shorten sales cycles.
What is the ROI of cybersecurity monitoring services for large enterprises?
ROI shows up as avoided downtime, reduced incident costs, faster audits, and higher win rates. Measure: MTTD/MTTR reductions, “customer-impact minutes avoided,” audit hours saved, and sales cycle time. Many enterprises see 10–25% faster closings after launching a Trust Center with live uptime and compliance status. Automation that closes benign alerts can reclaim 20–30% analyst time, which you can redeploy to hunts and engineering fixes.
Which is the top cybersecurity monitoring framework for compliance automation?
Use a control-based approach: map NIST CSF or ISO 27001 Annex A controls to specific telemetry and evidence. Pair with a compliance automation platform (Drata, Vanta, Hyperproof, AuditBoard) that pulls logs and screenshots automatically. The “best” framework is the one your buyers recognize. For US SaaS, SOC 2 often leads; for UK/EU, ISO 27001; for finance, add PCI DSS; for healthcare, HIPAA. Align evidence to controls and keep it evergreen.
Cybersecurity monitoring vs. security testing: What’s the difference for enterprises?
Monitoring is continuous; it detects and responds in real time. Testing is periodic; it validates design and controls (pen tests, red teaming, tabletop). You need both. Testing finds gaps so monitoring can add new detections and playbooks. Monitoring then proves fixes work in production. Treat them as a feedback loop: test → improve detections → monitor → learn → retest.
What are the best practices for cybersecurity monitoring to reduce business risks?
Go identity-first, normalize logs, write high-signal detections, and automate tier-1 response. Track MTTD/MTTR, signal-to-noise, and automation close rates. Run quarterly purple-team exercises and convert findings into detections-as-code. Publish a Trust Center and map evidence to SOC 2/ISO 27001 controls. Most importantly, tie each monitoring goal to a business KPI like uptime or conversion rate.
Can cybersecurity monitoring services improve lead generation and customer trust?
Yes. Prospects want proof, not promises. A live status page, clear scope of monitoring, and badges for SOC 2/ISO 27001 reduce perceived risk. Sales cycles shorten when procurement sees mapped evidence and response KPIs. Marketing content featuring incident response discipline and quarterly posture summaries boosts trust, demo requests, and win rates—especially in regulated sectors.
What is included in a cybersecurity monitoring checklist for Tier One companies?
Identity MFA, privileged access reviews; EDR/XDR everywhere; SIEM ingest from IAM/EDR/cloud/WAF/apps; detections for credential abuse, lateral movement, egress anomalies, and exfil; SOAR playbooks for isolation, token revoke, key rotation; CSPM/DSPM scanning; immutable backups; vendor and SaaS logging; evidence mapped to SOC 2/ISO controls; quarterly table-top tests with execs.
Cybersecurity monitoring jobs in the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia: What skills are in demand?
High demand for SOC analysts, detection engineers, threat hunters, incident responders, and cloud security engineers. Skills: detections-as-code (Sigma/Kusto), SIEM/XDR content development, SOAR automation, cloud security (AWS, Azure, GCP), identity analytics, and Python. Employers value storytelling too—turn alerts into clear business impact narratives for execs and customers.
What are real-world examples of cybersecurity monitoring in Fortune 500 enterprises?
Common patterns: identity-focused detections for compromised sessions, automated containment for endpoints, CSPM rules that block risky changes, and continuous evidence trails for audits. Many large firms run co-managed SOCs to guarantee 24×7 coverage across regions, publish Trust Centers with uptime and certifications, and conduct quarterly purple-team exercises that feed new detections into SIEM/XDR.
How do SOC teams use cybersecurity monitoring to increase efficiency and reduce downtime?
They standardize on a SIEM/XDR core, enforce detections-as-code, and automate enrichment and first actions (isolation, token revoke, DNS block). They measure MTTR and “minutes of impact avoided,” then surface those stats to leadership. Regular content sprints keep rules fresh. The result: fewer escalations, faster containment, and measurable uptime gains that protect customer experiences.
What is the top comparison between SIEM tools for enterprise security monitoring?
Focus on data economics, native integrations, query speed, detection content, and SOAR alignment. Splunk: powerful ecosystem, cost planning needed. Microsoft Sentinel: strong M365/Azure tie-ins and analytics. Google Chronicle: petabyte-scale search economics. IBM QRadar: mature correlation. Elastic: flexible stack and open tooling. Choose based on your cloud stack, identity platform, and ingestion profile.
